Membrane or implant that mimic healthy subchondral bone microarchitecture for treating joint-related diseases
Membrane or implant that mimic healthy subchondral bone microarchitecture for treating joint-related diseases
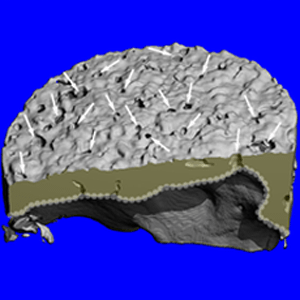
The present invention lies in the field of diagnosing and treating joint-related diseases. It provides for a membrane and an implant that mimic the healthy subchondral bone microarchitecture allowing for the regeneration of the joint’s bony and cartilaginous structures as well as its functionality.
read more