
Efficient fixation of pelvic ring fractures
The technology enables a simultaneous fixation of the anterior and posterior pelvic ring fracture, in combination with an adaptive force control and efficient compression of fracture gaps.
Challenge
The pelvis is a critical structure of the human skeletal system, as it transmits loads from the spine to the lower limbs through the sacroiliac joint. Gaps of the pelvic ring may arise as a result of injuries, in particular induced by a fracture or dislocation. Pelvic fracture is known as a serious injury of the human pelvis. Stable type A pelvic injuries with an intact pelvic ring can be treated with conservative methods (e.g. bed rest and lap belt) in combination with physiotherapeutic measures. However, type B or type C pelvic injuries require surgical measures, whereby the pelvis is typically first stabilized with an external fixator or a pelvic clamp in an emergency. External fixators are attached to the bone through the skin from the outside, with the aim to immobilize the fracture. However, available external fixation devices often do not allow for a sufficient and simultaneous stabilization of the anterior and posterior pelvic ring fractures. Moreover, known fixation devices do not provide a sufficiently adjustable compression of the gaps, which, however, can be crucial for a fast bone healing. Consequently, serious complications can occur, especially in the case of complex and unstable pelvic ring fractures.
Our Solution
Scientists from the University Medical Center Göttingen have invented a pelvic ring injury treatment device for a simultaneous fixation of the anterior and posterior pelvic ring fracture, which provides an efficient and adjustable compression of fracture gaps. The device comprises a telescopic bar with an adjustable length and two Schanz pins, which are mounted at the two ends of the bar. The length of the telescopic bar can be fixed after the desired length has been adjusted, in parallel to a specific sliding and fixation mechanism of the pelvic ring injury treatment device along the Schanz pins. The Schanz pins posses a degree of freedom for rotation, allowing for flexible and precise positioning. In connection with a pressurization device, a specific preload configuration and targeted forces are applied. This leads to the generation of joint forces, closure of any existing gap and the compression of the innominate bones at the anterior joint and the pressing of innominate bones against the sacral bone at the posterior joints of the pelvic ring.
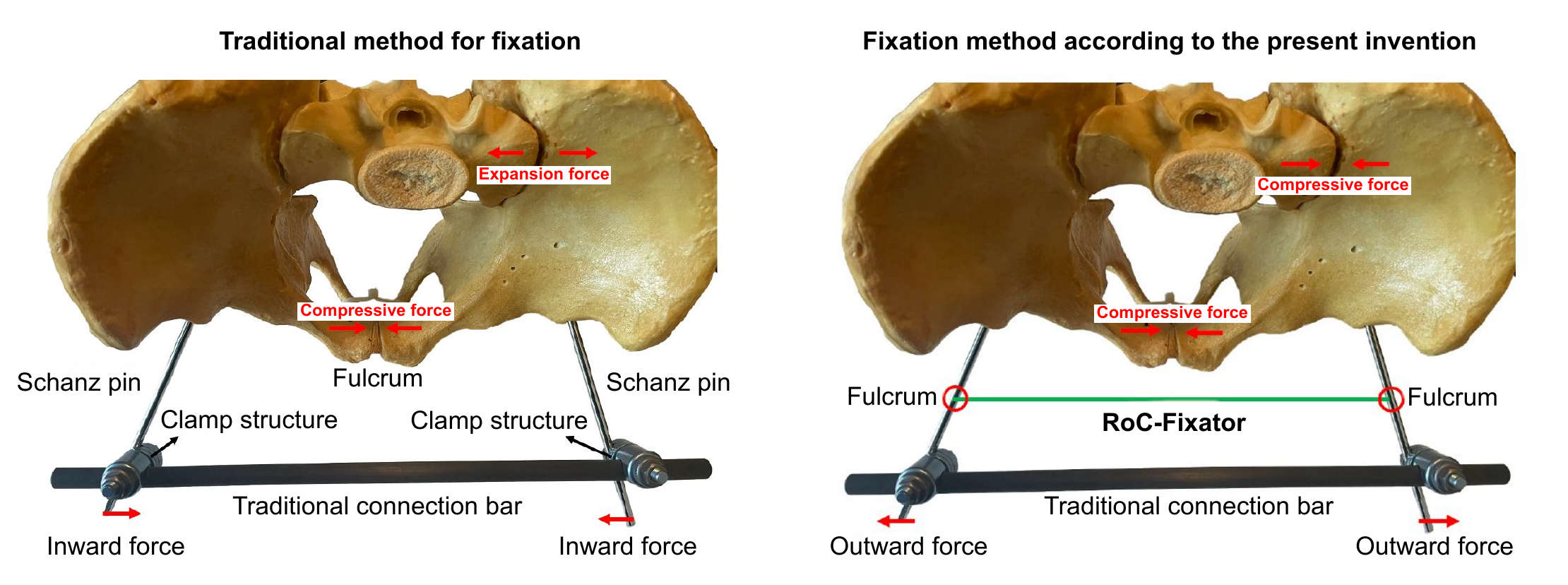 Traditional device and procedure for fixation of pelvic ring fractures in comparison to the device and procedure for the fixation of pelvic ring fractures according to the present invention and patent application (source: Prof. Lehmann, Prof. Schilling, Dr. Böker, Mr. Li and Mr. Zhou, University Medical Center Göttingen).
Traditional device and procedure for fixation of pelvic ring fractures in comparison to the device and procedure for the fixation of pelvic ring fractures according to the present invention and patent application (source: Prof. Lehmann, Prof. Schilling, Dr. Böker, Mr. Li and Mr. Zhou, University Medical Center Göttingen).
Advantages
- Simultanoeus fixation of the anterior and posterior pelvic ring fractures
- Optimized forces, moments, force ratios and/or moment ratios applied by the Schanz pins
- Adjustable force control and force feedback
- Device design with less complexity
- Optimized device weight
- Lower production costs in comparison to available fixation devices
- Reduced time for application
- More comfort for the patient in combination with a minimally invasive procedure
- Reduced risk of secondary injuries and complications
- Reduction of the required skills of the surgeon when using the device
Applications
- Fixation of pelvic ring fractures
Development Status
The fixation device has been successfully developed. Engineering drawings, 3D models and finite element simulation data are available. Prototype in development.
Patent Status
European patent application: EP24178411.5
Patent holder: Georg-August-University Public Law Foundation (University Medical Center Göttingen)
Contact
Dr. Mirza Mackovic
Patent & Innovation Manager Technology
E-Mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Tel.: +49 551 30724 153
Reference: CPA-2544-UMG
Tags: Physics and Technology & Software, Surgery, Medical technology
