
Hub and shaft-hub connection
A novel hub for a free from play transmission of relatively high torsional moments between a shaft and a hub is presented. Moreover, versatile applicable hubs are suggested, by considering manufacturing and supply effort and component variety.
Challenge
For connection of machine parts with cylindrical components (e.g. shafts or axles) form-fit and frictionally engaged hubs are used. Shafts and axles are often produced from metallic materials, while hubs are produced from metallic or (non-)reinforced plastics. A clamping hub can establish a free from play, frictionally engaged connection, whereby a pressing force is generated between the hub and the shaft. However, plastic clamping hubs, which are suitable for a free from play transmission of larger forces and moments, are widely unknown, since plastics can endure only relatively low compressive stresses. Consequently, in a frictionally engaged connection configuration the normal force is limited, which in combination with a comparatively low coefficient of friction between a metal shaft and known plastics allows to transmit only relatively low torsional moments.
Our solution
A scientist from the Ostfalia University of Applied Sciences has developed a novel hub and shaft-hub connection, which enable a free from play transmission of relatively high torsional moments between a shaft and a hub. According to the invention, the hub can be manufactured cost-efficiently in large quantity and is optimized with regards to weight, mass moment of inertia, costs, materials and fatigue limit. The hub base body can be manufactured by injection molding from a plastic or a fiber-reinforced composite material and contains a cut, which is limited by at least one inner surface and has a cylindrical shape. Moreover, the hub has a clamping jig, which is used to deform at least one inner surface of the base body, leading to generation of a normal and frictional force between the shaft and hub inner surfaces. The inner surface of the hub base body is not stabilized directly on the shaft, but by using a contact element. The contact element acts between the hub base body and the shaft, which is placed in the cut of the base body. As a result, the contact conditions can be tailored advantageously. The contact element forms a frictional coefficient with the skin surface of the shaft, which is higher than the frictional coefficient of the plastic and the (metallic) shaft. This embodiment causes, that when using the same normal force in the contact area, i. e. the same stress of the base body plastic, a higher friction and thus a higher transmittable torsional moment can be achieved. The contact element can be shaped as a shell, foil, sheet plate or coating. Hence, it can be adapted to the needed application. Furthermore, the present invention suggests a group of hubs and shaft-hub connections, which enable a connection with shafts with various diameters, while the individual hub base bodies do not need to be adapted individually. In fact, the invention suggests that the individual hubs exhibit identical base bodies, which exhibit identical inner surfaces. In combination, contact elements with different radial dimensions can be adjusted to different diameters of the respective shafts.
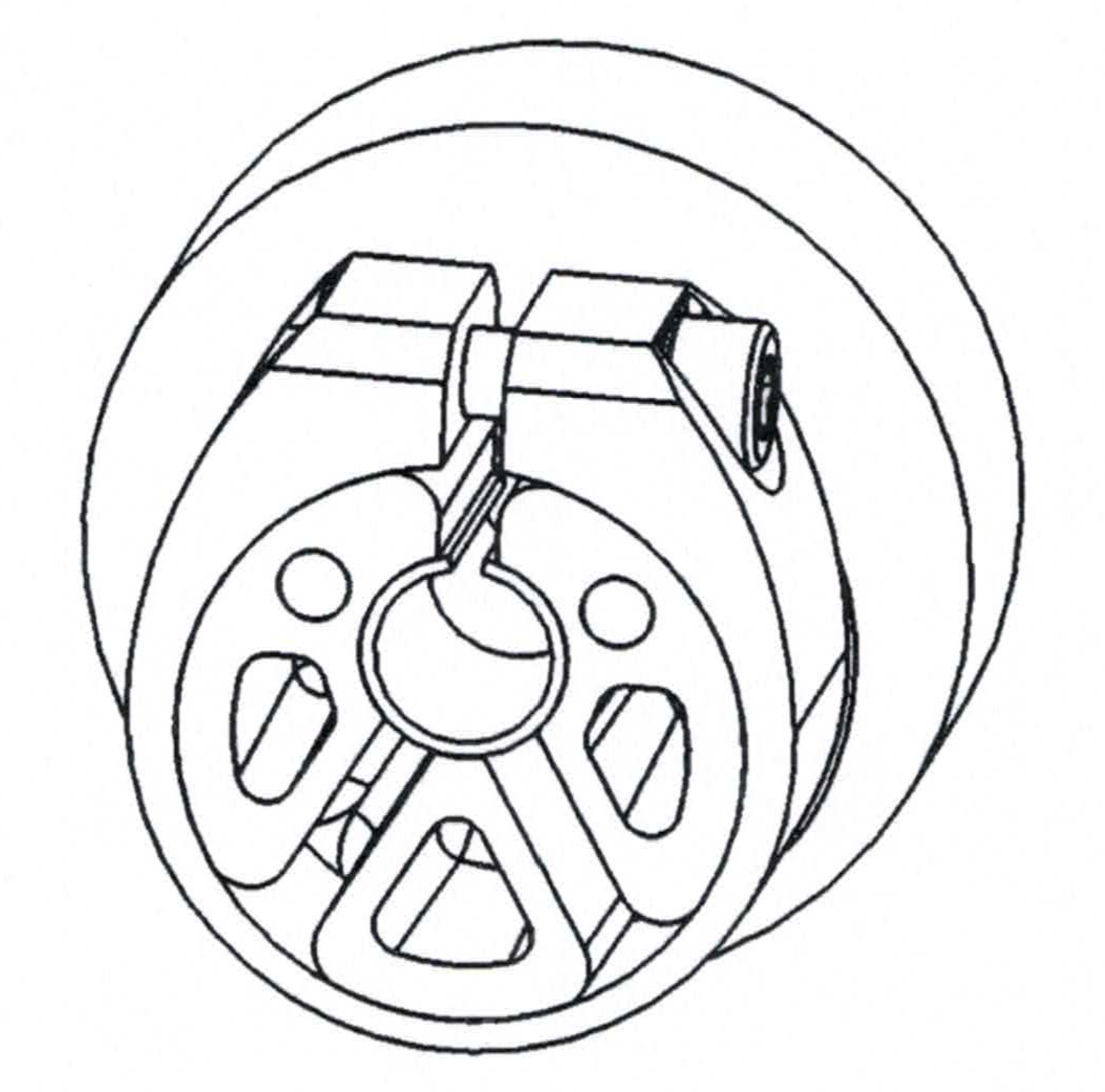
Fig. 1: Layout of the clamping hub according to the invention (source: Ostfalia University of Applied Sciences Braunschweig/Wolfenbüttel and adaptation according to DE102019116165B4).
Advantages
- Free from play transmission of relatively high torsional moments
- Cost-efficient production of the hub base body from plastic materials in high quantity
- Economic production of contact element from metallic materials
- Flexible system adaptation
Applications
- Compensating coupling
- Flange coupling
- Denture clutch
- Magnetic particle coupling
- Sprag clutch
- Friction clutch
Development Status
The technology has been successfully developed. System functionality experimentally approved. Prototype available.
Patent Situation
German patent application granted: DE102019116165B4
Patent holder: Ostfalia Universtiy of Applied Sciences Braunschweig/Wolfenbüttel
Contact
Dr. Mirza Mackovic
Patent Manager Technology
E-Mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Phone: +49 551 30724 153
Reference: CPA-2108-FHBW
